The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) decided yesterday, Tuesday, to raise interest rates by 25 basis points, as expected, from 3.60% to 3.85%, with expectations of continued monetary tightening. Recent Australian economic data show some resilience in economic performance, with the Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) at 52.3 points, slightly below expectations (52.4) but higher than the previous reading (51.6).
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) on a year-on-year basis rose by 3.80%, above expectations (3.50%) and the previous reading (3.40%). The unemployment rate fell to 4.1%, below expectations (4.4%) and the prior figure (4.3%), while net employment change increased to 65.2 thousand jobs, exceeding expectations (28.3 thousand) and the previous reading (-28.7 thousand).
The Australian dollar (AUD) traded at 0.7094 against the US dollar (USD) on Thursday, January 29, 2026, the highest level since February 2, 2023. The pair has risen about 6% since the beginning of the year and is currently trading above 0.7000.
The AUD continues its strong performance, leading G10 currencies against the USD, ahead of the New Zealand dollar, Norwegian krone, Swedish krona, Swiss franc, British pound, euro, Canadian dollar, and Japanese yen.
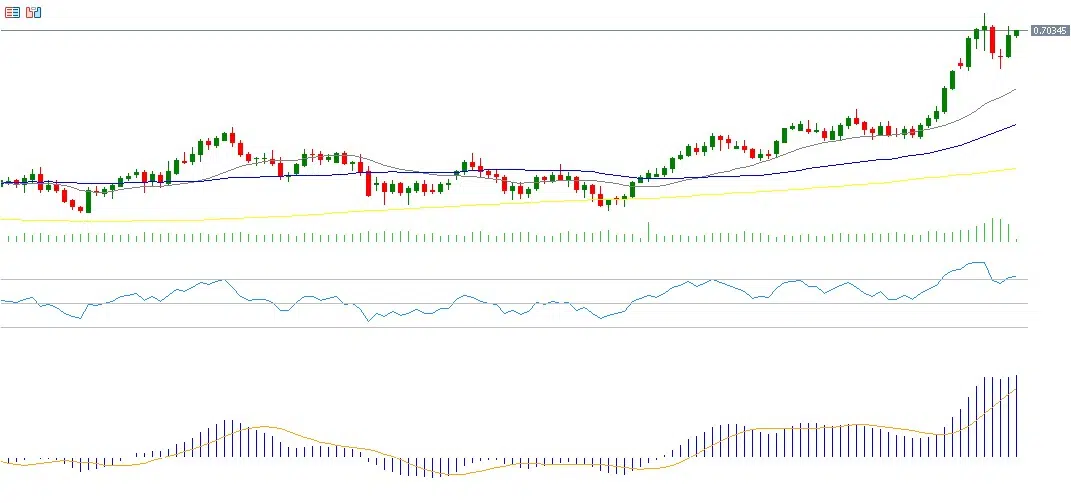
From a technical perspective, if the pair breaks the pivot level at 0.7006, it may test support levels at 0.6961, 0.6898, and 0.6853. If the pivot level is surpassed upward, resistance levels at 0.7069, 0.7114, and 0.7177 may be targeted.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) currently stands at 73 points, in the overbought zone, indicating positive momentum for the AUD/USD pair. The MACD shows a bullish crossover between the blue line and the signal line, supporting the likelihood of continued positive momentum.
Please note that this analysis is provided for informational purposes only and should not be considered as investment advice. All trading involves risk.